Abstract
Introduction: The percent deviation of immunoglobulin heavy chain gene variable region from the germline sequence (IGHV% or mutation status of IGHV) is commonly used as a prognostic factor in CLL. A 98% cutoff in IGHV %is used to classify CLL patients into mutated (≤98% identity or ≥2% deviation) with a favorable treatment outcome, and unmutated (>98% identity or <2% deviation) with an unfavorable treatment outcome. Because several studies identified dissimilar IGHV% cutoffs ranging from 1% to 5%, we wondered whether there is no universal IGHV% cutoff and the IGHV% is a continuous prognostic variable.
Methods: We analyzed the data of 203 patients with CLL enrolled on the original frontline FCR clinical trial. Karyotype analysis, exome sequencing and stereotypy status was not available for these patients as most patients were enrolled in the protocol 17 years ago. Testing of IGHV mutation status was performed by comparing the resulting IGHV sequence with the consensus germline sequence in the IMGT/V-QUEST database and the percent change of base pairs was calculated. Cox proportional hazard regressionmodels were used to identify any association between covariates and survival (OS and PFS). Using the IGHV% as a continuous variable, we also analyzed the outcome of patients treated with frontline FCR off protocol (n=332) and of patients treated with ibrutinib (n=166). Statistical analysis was performed using the Stata/SE version 14.2 statistical software (Stata Corp. LP, College Station, TX).
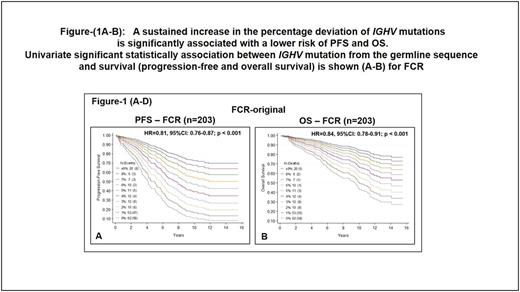
Results: The clinical characteristics of 203 patients treated with FCR on protocol and of 332 patients treated with FCR off protocol were similar. The median follow-up of patients enrolled on the original FCR trial was 10.7 years (range 0.1-15.5) and of patients treated with FCR off protocol was 5.6 (0.2-12.1) years. The mean number of treatment cycles was 6 (range 1-6) in both cohorts. Cox proportional hazard models showed the association between IGHV% , as a continuous variable, and survival (PFS and OS) in original FCR trial cohort (Figure 1A and B). The IGHV% was significantly associated with PFS (hazard ratio (HR) 95%; confidence interval (CI): 0.81 (0.76-0.87); P <0.001) and with OS (HR: 95%; CI: 0.84 (0.78-0.91); P <0.001), suggesting that as the percent deviation of IGHV from the germline sequence increases, the risk of disease progression or death significantly decreases. Similarly, in patients treated with FCR off protocol (n=332) there was a significant association between PFS (HR: 0.84; CI: (0.79-0.90); P <0.001) and OS (HR: 95%; CI: 0.90 (0.82-0.99); P <0.039) and IGHV% as a continuous variable. Multivariate analysis revealed that IGHV% as a continuous variable significantly predicted survival. High IGHV% levels were incrementally associated with favorable PFS and OS in both groups of FCR-treated patients combined (hazard ratio (HR): 95%; confidence interval (CI): 0.81 (0.76-0.87); P <0.001, and HR: 95%; CI: 0.84 (0.78-0.91); P <0.001, respectively). We conducted a similar analysis on 166 patients treated with ibrutinib. Although the number of patients was considerably small and their follow-up was only 2 years, the IGHV% as a continuous variable was not associated with PFS or with OS (not shown).
Conclusions: A continuous increment of IGHV% deviation predicts the survival of CLL patients treated with FCR. The higher the percent deviation, the better is treatment outcome, suggesting that the prognostic relevance of IGHV% is a continuous, rather than a dichotomized, variable. In sharp contrast, the IGHV% deviation does not appear to predict the survival of patients treated with ibrutinib.
Burger: Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie Company: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses; TG Therapeutics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses, Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel, Accommodations, Expenses. Tam: Abbvie: Honoraria, Research Funding; Roche: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen Cilag: Honoraria, Research Funding. Wierda: The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center: Employment; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; GSK/Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; Juno: Research Funding; Emergent: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Kite: Research Funding; Genentech/Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Genzyme: Consultancy, Honoraria; Sanofi: Consultancy, Honoraria; Karyopharm: Research Funding; Acerta: Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; Merck: Consultancy, Honoraria. Thompson: Pharmacyclics: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Jain: Genentech: Research Funding; Servier: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Novimmune: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; ADC Therapeutics: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Abbvie: Research Funding; BMS: Research Funding; Verastem: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding; Adaptive Biotechnologies: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Incyte: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding. Kantarjian: Delta-Fly Pharma: Research Funding; ARIAD: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Bristol-Meyers Squibb: Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding. Cortes: ImmunoGen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Sun Pharma: Research Funding; Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: Consultancy, Research Funding; ARIAD: Consultancy, Research Funding; Teva: Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding. O'Brien: Astellas: Consultancy; Vaniam Group LLC: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; AbbVie: Consultancy; Gilead Sciences, Inc.: Consultancy, Other: Research Support: Honorarium, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Other: Research Support: Honorarium, Research Funding; Acerta: Other: Research Support: Honorarium, Research Funding; Sunesis: Consultancy; CLL Global Research Foundation: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Consultancy; Aptose Biosciences, Inc.: Consultancy; GSK: Consultancy; Celgene: Consultancy; Regeneron: Other: Research Support: Honorarium, Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Consultancy, Other: Research Support: Honorarium, Research Funding; ProNAI: Other: Research Support: Honorarium, Research Funding; Alexion: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal